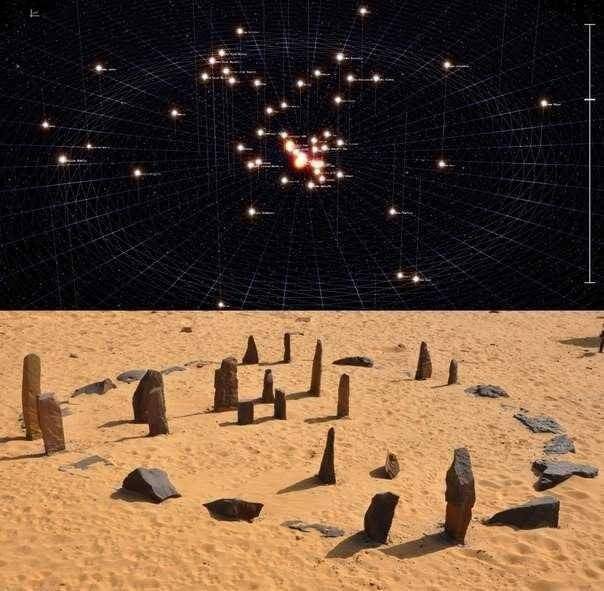
Located 500 miles south of Cairo, deep in the Nubian desert, is one of the oldest stone circles in the world. Research has revealed that the Nabta Playa complex dates before Predynastic Egypt.
Nabta Playa is unique not only for its age but also the ancient astronomy coded into its alignments. It could be evidence of the first Egyptian civilization to use astronomy.
If it is the origin of Ancient Egyptian Astronomy, it may provide the earliest signs of the Egyptian civilization itself.
The mystery of the ancient Egyptian Stone Circle
If you didn’t know better, you could easily miss the Nabta Playa stone circle. Discovered in 1974, anthropology professor Fred Wendorf was returning from an expedition from Libya. He and his party nearly crossed the rock formation without noticing. After an initial investigation, instincts told him there was something significant about Nabta Playa.
Located deep in the Nubian Desert, the area is one of the most inhospitable in Egypt. It is isolated by miles of dry, barren sand that endures extremely high temperatures.
It wasn’t always like this. In ancient times the Nabta Playa region was once home to annual rainfall which brought with it seasonal lakes and livable landscapes. Around 11,000 years ago that the monsoons of Central Africa moved north. They brought a water source into the regions of southern Egypt.
Returning to the site, Wendorf’s revealed the stones to be quartzite sandstone. These were likely brought from the open zone of ancient sandstone mining, located one kilometer away. Ancient practices beyond a hunter-gatherer society were previously unidentified across Egypt in this time.
Nabta Playa was beginning to reveal its secrets. In 1980, archaeologists, using a GPS, examined the stone circles formations. Their results found ancient wisdom within their alignments. The large radial stones were placed with their exact position in the north-south, east-west cardinal directions. Their layout was similar to the calendar circle stones at the Karnak temple.
The first civilization of Ancient Egypt?
The Nabta Playa site shows evidence of a society not previously recorded in ancient Egypt. Around 7500 years ago, the area was home to a population of people with cultural practice.
The megalithic structures remain the most valuable remnants of a lost culture. Found within the area are stone circles, burial chambers, as well as megalithic and carved standing stones. So far, at least 30 of these structures have been uncovered.
In what is now named the “Valley of Sacrifices,” there are ten mounds of broken sandstone blocks. The chambers beneath them contain remains of cattle, goats, and sheep.
The largest and perhaps oldest contains an entire cow in an elaborate chamber covered by a tamarisk roof. The carcass is orientated roughly north-south, lying on its left side, with its head west.
At around 8000BC, the first signs of human occupation begin to appear in the region. It is this area where the oldest evidence of animal agriculture is found on the African continent.
Nabta Playa appears to be a center of cultural evolution of the Egyptian civilization. From the burial mounds to farming, and animal husbandry, the first sprouts emerge at Nabta Playa.
Studies reveal signs of occupation in the area for thousands of years. Geologists explain the climate was cycling from very arid and harsh to seasonally wet and habitable every few thousand years.
Weather could have been a factor for a cycle of cultures living in the area. Excavations show long spans of time passing without any artifacts found. Then, something happened at 3000BC (5000 years ago). It’s here the last signs of human occupation are recorded at Nabta Playa.
The Ancient Astronomy of Nabta Playa

Nabta Playa could be the origin of Ancient Egyptian Astronomy.
Of the many stone structures found at Nabta Playa, the stone circle is most well-known.
The circle is made up of four gateways, two aligned North-South, and two pointing East-West. These alignments were likely used to track the summer and winter solstices, as well as vernal and autumnal equinoxes.
This would have been of extreme importance to the inhabitants of Nabta Playa at the time. The agricultural year would be based on when the wet season was approaching.
There was, however, more purpose for the site. In the middle of the stone circle is six anomalous stones that do not align to any of the four cardinal points.
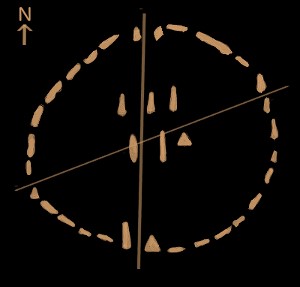
North-south alignment of the Nabta Play Stone Circle.
The Archaeoastronomy of Nabta Playa
Nabta playa could be one of the earliest astronomical observatories found in Egypt.
The study of archaeoastronomy is a relatively new discipline in science. Scholars analyze archaeological sites and their astronomical connections.
For lost ancient civilizations, the knowledge of the movements of the stars was held in utmost importance. Evidence shows that as it helped shape and develop cultures all over the world.
Astrophysicist Thomas Brophy has been at the forefront of researching the astronomy of Nabta Playa.
Of the six mysterious standing stones in the center of the stone circle, it is now thought they are part of an ancient star map. Each stone seems to represent a star in the sky. Studies reveal the stone circle acts as a map for accurate angles and distances to relative stars.
Most curiously, Nabta Playa shows knowledge of precession of the equinox. It’s the much larger cycle of the star constellations in the sky comparative to the sunrise on the spring solstice.
Just before the sun rose on the summer solstice around 5000BC, three of the stones in the center of the stone circle would have lined up perfectly with the belt stars of the constellation of Orion. This time marks when the precession cycle is at one extreme.
12,000 years earlier, the opposite extreme of the precession cycle occurs. Again, the other three stones line up precisely with the shoulder stars of Orion. The stone circle is an accurate astronomical map tracking time back to around 16,500BC.
Ancient Egyptians at Nabta Playa were recording the movements of the constellation of Orion’s Belt as a way to mark the precession of the equinox.
Ancient Egyptian astronomy
The ancient Egyptians knowledge of the sky went far beyond seasonal cycles.
Not far from the stone circle at Nabta Playa are further signs of ancient astronomy. Several clusters of standing stones have been found in groups in a runway formation from a central viewing stone. It is thought that this viewing stone was used to track and site different stars.
From the viewing stone, each visible stone is not only marking a specific star of the sky. It also marks the correct distance that star is situated from earth. As a scaled-down model, when applied to the modern astronomical measurements, it is an astonishing match.
Today, researchers can estimate the night sky as it would have looked at the time Nabta Playa was inhabited. Using this data, at the time of sunrise on the Spring equinox, they found a correct match for the heliacal rising of the stars indicated by their corresponding stone.
For the ancients, just before the sun appeared on the horizon, the star relative to its stone would have risen perfectly overhead.
Conclusion:
The Nabta Playa site is an archaeological mystery for many reasons. Much of the area may never be excavated due to the harsh desert conditions of the desert. What has been uncovered may prove to be the earliest signs of Egyptian civilization.
Predynastic evidence of burial and sacrificing that do occur in Egyptian civilization, show it could be the precursor. However, the depth of the ancient astronomy is nothing short of incredible. How this lost society was aware of the motions and distances of stars from earth is puzzling in its complexity.
Were these people the first Egyptian Astronomers? Today we simply don’t know how the ancient people of Nabta Playa had such an understanding of highly advanced astronomy.
Now it’s up to you. What does the Nabta Playa stone circle reveal of early Egyptian history?
Sources:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278416598903191
- http://adsbit.harvard.edu//full/2007AfrSk..11….2M/0000003.000.html
- https://www.amazon.com/Origin-Map-Prehistoric-Megalithic-Astrophysical/dp/0595241220

 Located deep in the Nubian desert, the Nabta Playa stone circle holds astonishing details of ancient astronomy.
Located deep in the Nubian desert, the Nabta Playa stone circle holds astonishing details of ancient astronomy.