Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland. Its main role is to regulate sleep-wake or circadian rhythms.
Recently, researchers have found the pineal gland to be the main endocrine gland of the body. Secretion of melatonin influences far more than sleep throughout the body.
From the immune system to weight gain, and fertility, melatonin plays a role for all organs.
Low melatonin can be a sign the pineal gland is not producing enough. It is linked to disrupted sleep cycles. Other conditions can increase the risk of low melatonin. Endocrine disorders may interfere with melatonin release and use.
Melatonin can be used to help those at risk of low melatonin.
In this article, we’ll outline what melatonin is used for.
Causes of low melatonin:
- Stress
- Lack of exposure to natural light during the day or working indoors.
- Exposure to blue light at night (often from television, phones, computers, and clocks)
- Working night shift
- Travel and time zone changes (also known as jet lag)
- Lack of sleep (i.e., parents and those with high-pressure jobs)
- Leaky gut, intestinal permeability, and nutrient deficiencies
- Caffeine
- Tobacco
- Mutations in AANAT or ASMT genes.
- SSRI’s (Prozac and fluoxetine)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Beta-blockers
- NSAIDs such as Aspirin, ibuprofen, Aleve, Motrin.
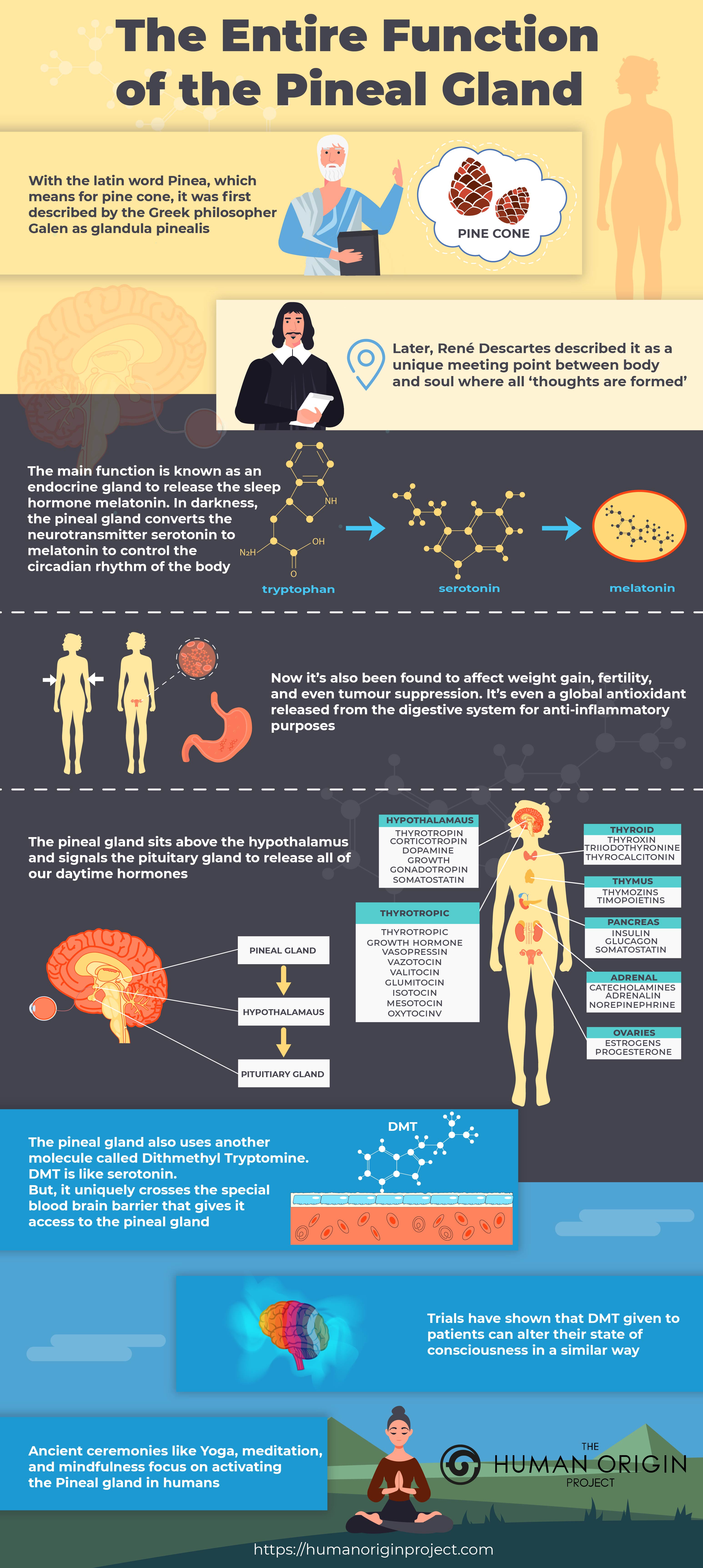
14 benefits of using melatonin
1. Melatonin to sleep better
Melatonin for sleep is the best-known reason to supplement. When you prepare for sleep, the body should release melatonin. It may be one of the best natural sleep remedies. (1)
Does melatonin help you sleep?
Long-term, melatonin may not be the answer for better sleep.
As a hormone, there are downsides to taking melatonin to sleep. When you take a melatonin supplement, it can decrease melatonin production in the pineal gland. Long-term, you want to boost melatonin release naturally.
How long should you sleep after taking melatonin?
Melatonin levels stay high in the body for 12 hours. If you take melatonin 30 – 60 minutes before bed, you should sleep roughly 8hrs.
2. Melatonin to cure insomnia
Studies show that melatonin 3mg can cure insomnia. (2) It may also improve morning alertness in the elderly.
3. Melatonin to cure jet-lag
Taking melatonin supplements may reduce insomnia related to jet lag. (3) A melatonin supplement must be taken to aline with the evening of the new time zone.
When to take melatonin for jet lag: 30-60 minutes before bed for most effective use.
4. Can melatonin help depression?
Disrupted sleep cycles can increase the risk of depression.
Studies show melatonin could help reduce symptoms of seasonal depression by assisting the sleep cycle. (4)
5. Is melatonin good for anxiety?
Sleep deprivation can associate with anxiety-like behavior. Research has shown that melatonin treatment may prevent these symptoms. (5)
6. Melatonin for stomach ulcers and heartburn
Melatonin and L-tryptophan have been shown to be protective of the digestive system. Studies show melatonin may help heal stomach ulcers associated with aspirin. (6)
Melatonin may help increase gastrin levels. Gastrin has anti-inflammatory action on the digestive system.
7. Melatonin as an anti-cancer and tumor treatment
The immune system is known to be influenced by stress hormones. Low melatonin is found in women with breast cancer, and men with prostate cancer.
Melatonin may have an anti-tumor role on the immune system. Studies show melatonin therapy may reduce the risk of death in certain cancer types. (7)
8. Melatonin may help with weight loss.
Melatonin supplements may help decrease fat storage. The likely mechanism an increase in the release of the hormone leptin. Studies looked at oral melatonin may help with weight reduction in post-menopausal women. (8)
9. Melatonin to reduce blood pressure
To induce sleep, melatonin acts to decrease blood pressure.
Doses of melatonin have been shown to reduce blood pressure in men and women. (9) These changes may be temporary.
10. Melatonin to boost memory
Deep restful sleep helps form new memories. Melatonin may decrease stress and improve sleep for better memory formation. (10)
11. Melatonin to reverse tinnitus
Studies show melatonin may be a safe and effective treatment for tinnitus (11).
12. Melatonin as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent
Melatonin acts as a broad-spectrum antioxidant. It is also an anti-inflammatory agent. Melatonin supplementation was found to suppress exercise-induced inflammation. (12)
13. Melatonin for eye health
Melatonin could lower the risk of eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). (13)
14. Melatonin to boost human growth hormone
Human growth hormone is naturally released during sleep. In healthy young men, taking melatonin may help increase growth hormone levels. (14)
Conclusion
While many of the benefits of melatonin relate to sleep there are far-reaching uses of melatonin.
Melatonin has benefits all over the body.
To read more:
- The Pineal Gland
- What is melatonin?
- How to use Melatonin for Sleep
- Decalcify your pineal gland and open the third eye.
Now it’s up to you.
What role of melatonin have you found most useful?
Leave your thoughts in the comment section below.

 Melatonin is the hormone made in the pineal gland. It is used for many health benefits
Melatonin is the hormone made in the pineal gland. It is used for many health benefits