Melatonin is released from the pineal gland to help the brain prepare for sleep. Many people take melatonin for sleep however supplements aren’t always successful. It’s important to know the circadian rhythm that assists the brain and body to sleep.
Melatonin for sleep works in two main ways:
- Manages the circadian rhythm or light-dark cycle within the body
- Prepares physical sleep process
To fully understand melatonin for sleep, we must look at the pineal gland.
As the master endocrine gland in the human brain, the pineal and sleep cycle oversee nearly all processes in the body.
Melatonin is the pineal gland’s tool to help tune the body to the day-night cycle. It schedules other organs to do the same.
In this article, we’ll outline how melatonin for sleep works in the brain and body.
What is your circadian rhythm?
As humans live on planet earth, our body is connected to day-night cycles. Melatonin and sleep are our own processes to live alongside the earth’s orbit around the sun.
Circadian rhythm is the biology that tunes your body to the cycles of day and night. It’s 24-hours long, as the earth rotates the sun, and is also called diurnal rhythms.
Melatonin is the hormone by which our body lives within the day-night cycle of planet earth. The release of melatonin tells the brain it’s time to sleep.
How does your body make melatonin?
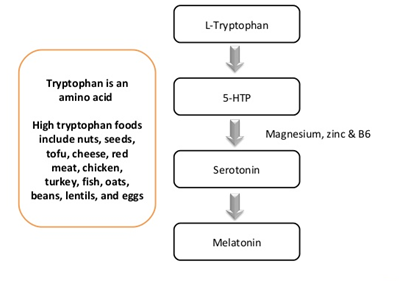
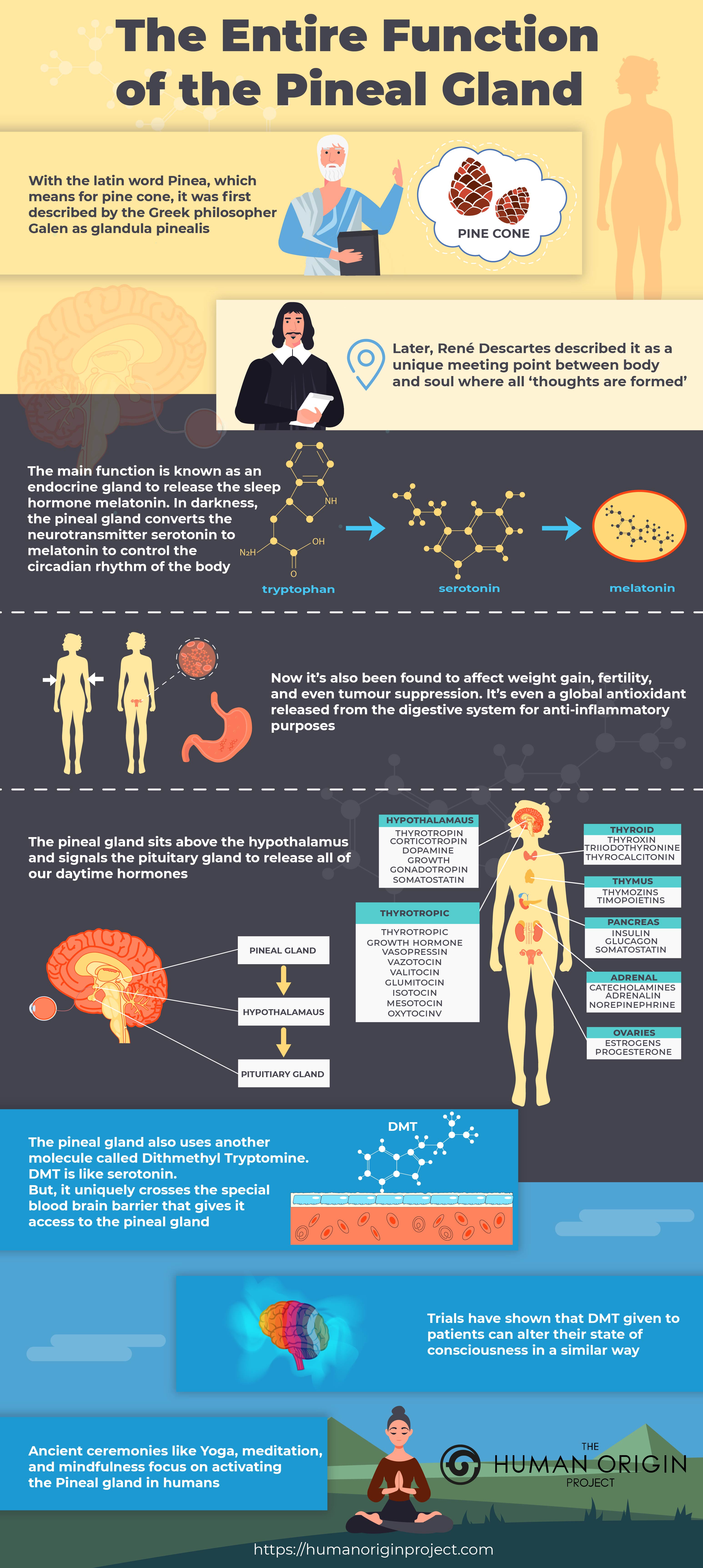
Melatonin for sleep is made via the amino acid tryptophan in the pineal gland of the brain.
Melatonin is made using a four-step pathway from the amino acid Tryptophan. You can obtain tryptophan from your diet.
Tryptophan converts to melatonin in the pineal gland. First, it is made into tryptamine. Then converted to serotonin. Serotonin is then made into melatonin.
Tryptophan -> Tryptamine -> Serotonin -> Melatonin
The pineal gland then releases melatonin into the bloodstream.
Melatonin is released in other areas of the body like the digestive system. However, the pineal gland is the only place it is released to the bloodstream.
What triggers melatonin release?
Darkness, or the absence of light, activates melatonin production in the pineal gland.
As the third eye, the pineal gland detects light from the two eyes. Light sends a neural signal that travels via the hypothalamus (SCN) to the pineal gland.
It takes four hours for melatonin levels to peak or fall. These cycles are the circadian rhythm. Darkness begins the cycle and can be disrupted if artificial light is present.
Here’s how the rise and fall of melatonin release happens.
- Evening: Melatonin levels begin to rise
- Night time: Melatonin levels peak for sleep
- Morning time: Melatonin decline to prepare for waking.
How the release of melatonin for sleep works
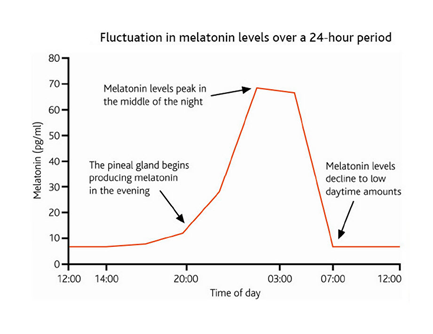
In the evening, it takes four hours for blood levels of melatonin for sleep to rise.
The circadian rhythm encodes the rise and fall of the sun within the body. Melatonin is the darkness hormone. If you can imagine the organs and brain inside the body, they can’t see the outside world. When melatonin levels rise, they know it’s time to prepare for sleep.
At night time, you sleep better when you are cool and relaxed. Melatonin regulates the body to enhance these conditions.
Here’s how melatonin for sleep works:
Melatonin affects blood pressure, body temperature and hormone levels.
It works by:
- Decreasing blood pressure for sleep
- Decreasing body temperature for sleep
- Decreasing waking and stress hormones for better sleep (like cortisol)
- Decrease dopamine levels in the eyes which is a hormone that helps you stay awake (1)
By cooling, calming, and relaxing the body, melatonin prepares the brain and body for sleep.
Is serotonin involved in sleep?
Serotonin does affect sleep. It is the precursor for melatonin.
The pineal gland creates the balance between melatonin and serotonin. Melatonin is made in the pineal gland from serotonin. It’s a conversion that is driven by the presence of light.
As sunlight hits the eye, it projects to the hypothalamus (SCN) and stops melatonin production. Light decreases melatonin levels. As darkness begins, the SCN signals the pineal gland to produce melatonin.
When melatonin levels rise, serotonin in the pineal gland fall. However, it doesn’t happen straight away.
The pineal gland begins to convert serotonin in response to darkness. Serotonin begins to decrease four hours before the rise in melatonin increase.
When the eye is exposed to light, it triggers the release of vitamin D which helps convert tryptophan to serotonin.
Serotonin is converted to tryptamine to melatonin once it is dark.
It is a cascade that takes time once darkness begins in the early evening.
The rise of melatonin is delayed four hours after the decrease of serotonin.
Is melatonin safe for sleeping?
Now we understand how melatonin for sleep works. We see that it’s produced in the pineal gland. The best way to boost melatonin is via natural foods and healthy sleep habits.
Taking an oral melatonin supplement is safe for sleep. However, there are drawbacks. Remember melatonin is a hormone.
Taking a melatonin supplement can decrease the body’s natural production of melatonin.
Studies show melatonin supplements do increase blood levels of melatonin. A melatonin supplement for sleep may work in the short term. In the long-term, it can decrease the natural production of melatonin.
If you suffer from chronic sleep disorders, it can take some time to achieve healthy melatonin levels. In these cases, an oral melatonin supplement for sleep may be beneficial.
The best approach to melatonin for sleep is:
- Aim to boost natural melatonin
- Use of a melatonin supplement for a short period if needed
How do you get melatonin naturally for sleep?
Here are 13 steps to boost melatonin for sleep naturally
Remember: Always consult a physician before taking making taking any supplements or medications.
1. Get plenty of morning sunshine.
Sunshine helps the circadian rhythm to set. Rising early and exposing yourself, including the eyes, to the sun helps the body to begin the inner diurnal rhythm.
2. Take away artificial light and screens.
Blue and artificial lights stop the natural production of melatonin.
To increase natural melatonin production:
- Turn off most lights after 6 pm.
- Put screens to night time mode
- Use artificial light blocking glasses
- Sit in a dark, cool room before bed
3. Eat foods high in melatonin.
What foods are high in melatonin?
- Bananas
- Morello cherries
- Porridge oats
- Sweet corn
- Rice
- Ginger
- Barley
- Tomatoes
- Radishes
Eating these at night may help boost natural melatonin levels.
Ginger tea is a great way to produce melatonin naturally.
4. Eat foods rich in tryptophan.
The pineal gland converts tryptophan to melatonin. One way to boost melatonin is eating foods rich in tryptophan.
However, you still need to allow enough access to darkness for the pineal gland to convert to melatonin.
Foods rich in tryptophan:
- nuts
- seeds
- cheese
- red meat
- chicken
- turkey
- fish
- oats
- beans
- lentils
5. Decrease alcohol intake
Alcoholics are known to have decreased melatonin levels. (2) While you can still consume alcohol, try to have 3-4 alcohol free days per week to maximize natural melatonin release.
6. Decrease caffeine consumption after 2-3pm in the afternoon
Caffeine is a stimulant and has the opposite effect of melatonin in the body. Try to have caffeine in the morning to fit in with natural melatonin cycles. If you are sensitive to caffeine it may be wise to decrease your intake.
7. Take a magnesium supplement.
Magnesium helps block the stress hormone cortisol in the brain. It helps the process of sleep and enhances melatonin activity.
Try taking 400-600mgs of magnesium citrate or magnesium glycinate in the evening.
8. Take an L-Theanine supplement.
L-Theanine is an amino acid found in tea leaves. It helps produce more GABA in the brain. GABA produces alpha brain waves linked to wakeful relaxation. These begin the process of the states of consciousness of sleep.
Some studies show L-Theanine can improve sleep, reduce stress and anxiety. (3)
For sleep, stress and other uses: 500-1000 mg of L-theanine.
9. Take a glycine supplement.
Glycine is an amino acid and neurotransmitter. It can stimulate and depress neural activity. Studies show it can improve sleep quality. (4)
In the body, glycine decreases temperature under the skin. When you cool the body, it helps increase melatonin release.
For glycemic and sleep benefits, take a dose of 3-5 grams of glycine with meals and before bed.
10. Take a zinc supplement.
Zinc has calming and anti-depressant effects. You can take a dose of 30-50mg at night.
11. Take a vitamin B6 supplement.
Vitamin B-6 helps to metabolize zinc. Try taking 5-10mg combined with zinc. B-6 can induce vivid dreaming which may disturb sleep.
12. Take a vitamin B-12 supplement.
Vitamin B-12 speeds the rate at which you produce melatonin at night. Take a sublingual B-12 supplement in the right form (methyl-cobalamin not cyanocobalamin).
The dosage of vitamin B-12 is 1000–5000 mcg methylcobalamin held under the tongue for several minutes.
13. Exercise for better sleep
Daily exercise helps circadian rhythms to release melatonin for sleep in the evening.
When to take a melatonin supplement
For certain conditions, studies have shown a melatonin supplement can help sleep.
Causes of low melatonin include:
- Exposure to blue light at night.
- Caffeine consumption
- Tobacco
- Mutations in AANAT or ASMT genes
- SSRI’s (Prozac and fluoxetine)
- Calcium channel blockers
- BETA blockers
- Aspirin, ibuprofen, aleve, motrin
Conditions that may indicate to take melatonin.
- Insomnia (5)
- Poor sleep quality (6)
- Reduce jet lag (7)
- High blood pressure (8)
- Stomach ulcers (9)
- Stress, anxiety and mental health (10)
- Reduce tinnitus (11)
How much melatonin should I take to go to sleep?
Try all of the steps above to increase melatonin naturally. If you don’t have success, some studies suggest melatonin supplements can help for sleep.
Remember: Always CONSULT A PHYSICIAN BEFORE TAKING A ANY SUPPLEMENT.
Melatonin is a hormone, and while it may work, you should take a hormone long term.
Studies show dosage of melatonin between 500mcg and 3-5mg are shown to be effective.
Natural melatonin doses are closer to 250mcg.
The benefits of melatonin are not dose-dependent – taking more will not help you fall asleep faster.
When to take melatonin
Melatonin goes through a daily cycle of peaks and lows. You should know when to take melatonin to maximize your chance of sleep.
The best time to take a melatonin supplement is 30-60 minutes before bed. It allows levels to rise and for the body to prepare for sleep.
How to take melatonin for sleep
Always remember you are finding out how much melatonin your body needs to sleep.
Sit in a cool dark place at least two hours before bed. Play relaxing music, smile, and breath deeply.
5 Steps for melatonin for sleep:
- 30-60 min before bed take an oral melatonin dose of500mcg (0.5mg).
- If the dosage doesn’t work increase in 500mcg increments.
- Take a maximum dose of 5mg (10x the original dose).
- Plan to decrease your melatonin supplement after two weeks.
- Decrease by 500mcg, until you sleep without a melatonin supplement.
What are the side effects of melatonin for sleep?
As a hormone, melatonin supplements can induce side-effects.
Side effects of melatonin include:
- headaches
- nausea
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- irritability
How long does melatonin stay in your body?
Oral melatonin can remain in the body for about 12 hours. It stays in your system through the whole night until levels fall during the waking hours.
How to test melatonin levels
Melatonin is released in the night. As it enters the blood from the pineal gland, the body processes it in kidneys then the bladder.
Typically, in healthy young adults, melatonin levels during the day are very low (~1-10 pg /ml)
In the evening melatonin levels rise to (~40-100 pg /ml.)
Waking urinary levels or morning melatonin levels indicate hormonal levels at night
Melatonin levels can be tested with a morning urinary sample.
A nighttime urinary sample won’t show melatonin levels because the hormone has not reached the urine yet. Bed-time melatonin samples reflect the last couple of hours before bed.
Conclusion
Taking melatonin for sleep can be effective. However, it should never be considered a long-term solution.
For better sleep, you should aim to increase melatonin levels naturally. The best way to do this is to understand the function of the pineal gland.
To read more, here is an article on:
This article is meant for informational purposes only. It should never replace advice from a qualified physician.
Before taking any supplement, you should consult professional medical advice.
Has melatonin helped you get better sleep?
Leave your comments in the section below.

 The pineal gland releases the neuro-hormone melatonin for sleep. It is in delicate balance with the circadian rhythm.
The pineal gland releases the neuro-hormone melatonin for sleep. It is in delicate balance with the circadian rhythm.