For nearly 4.5 billion years the story of earth goes. Through much of its lifespan, the planet looked vastly different than today. In its early life, there was no water, no oxygen, no land, and no life.
The earth then formed in violent circumstances. Its earliest period remained chaotic and semi-apocalyptic for millions of years. The planet was molten hot and bombarded with incoming objects from space. In these early episodes of earth’s life was during the time the planet itself was still taking shape.
Let’s explore the story of earth.
How did the atmosphere form around the Earth?
About 4.1 billion years ago the planet began to settle down. It was then that time earth locked into an orbit around the sun. From here the surface began to cool down slightly. It was around this time that the first atmosphere started to take shape.
Unlike the fresh air we enjoy today, early earth’s atmosphere was unstable and poisonous. Made of elements like nitrogen, sulfur, hydrochloric acid, some water vapor and carbon monoxide among others.
It wasn’t until the planet began to cool off slightly that the atmosphere began to stabilize. Water, previously vaporized, was able to take a liquid form and the result was oceans spanning over the entire planet.
As this was happening, intense volcanic eruptions disturbed the earth, and huge clouds covered the skies, meaning rainfall and more cooling.
When did land first appear on Earth?
In the next stage, rocky terrain began to form. The atmosphere started to mix and steady. Now the first signs of life appear as simple bacteria. Evidence of these creatures are the only real evidence scientists can use to gauge this period.
For around 1 billion years microbes would be the only form of life that could survive the toxic atmosphere of earth.
Landmasses continued to grow as volcanic eruptions spat out molten lava that would become rock, and the earth slowly took on an appearance more like today.
When did oxygen appear on Earth?
Around 2.5 billion years ago, oxygen appeared. As more sunlight was able to penetrate the earth’s atmosphere, it brought the first opportunity for photosynthesis.
Oxygen formed made by simple blue-green algae known as cyanobacteria. They are thought to be the first oxygen creating organisms to live on earth. The air we now breathe is all due to these tiny microbes.
It was over the next billion or so years that things began to move along. Earth became more and more stable, with more photosynthesis filling the atmosphere and oceans with oxygen. Levels rose, although atmospheric oxygen was still as low as 5%.
Rodinia the first supercontinent
As oxygen rose, continents were starting to appear. It was the time that the first supercontinent ‘Rodinia’ took shape. Up until this point, the earth was made up of as much as 95% water.
Life on this supercontinent wasn’t very advanced. Simple algae and bacteria were thought to be the only organisms to live there. Violent conditions made life on earth difficult. Storms plagued the land alongside intense radiation and floods.
Around 350 million years later, heat and pressure building beneath the continent hit critical mass. The crust below Rodinia ruptured, and the first great supercontinent was no more.
Pangaea the next supercontinent
After Rodinia broke up and drifted apart, oceans formed between the new landmasses. Over time, the land changed its course and was brought back together forming the supercontinent Pangaea some 225 million years ago.
The seven continents that make up earth today are remnants of Pangaea. One day, millions of years in the future, the continents will drift back together, and a new supercontinent will form.
What were the first forms of life?
The bacteria that increased oxygen levels were creating a less toxic atmosphere was born. Complex life began to evolve, and single-celled organisms began to develop around 1.5 billion years ago.
Eventually, these simple life forms split and began to evolve separately. All animals, plants, and fungi trace back to this time. It’s difficult to pinpoint what order and the exact way this occurred.
When did multicellular organisms first appear?
Around 900 million years ago multicellular life evolved. It’s unclear how, but it did, and it took millions of years to happen.
After a slow start, the evolution of life on earth began to speed up.
The oceans were home to lots of varied forms of life. Sponges, simple jellyfish, ancient worms, starfish, and coral, all began to appear after splitting and evolving separately from their multi-celled ancestors.
New species and organisms flourished under the oceans then making their way onto the land.
Around 500 million years ago that the first organisms set foot upon the earth’s surface. The massive step in evolutionary terms began the process for plants and trees to develop. The oldest fossilized tree remains date to 385 million years ago.
Four-legged animals followed soon after. Then fish, reptiles, ancient mammals and amphibians.
Cataclysmic cycles and the evolution of life
Throughout earth’s history, life is interrupted by great cataclysms that rock the very foundations of the planet. Meteorite and comet impacts have nearly wiped out all living things. One of these events rocked the earth 250 million years ago, causing the first great mass extinction event.
It paved the way for new organisms to take over where their extinct ancestors left. After this extinction event, it was the dinosaurs to populate the earth. They were the dominant species on the planet for millions of years, growing to enormous sizes. The largest known animal to ever walk the earth lived during this time, known as the giant sauropod.
As dinosaurs were at the top of the evolutionary tree, another cataclysm rocked the earth. Sixty-five million years ago saw the once dominant animals reduced to nothing but fossils. From this point on mammals became the dominant species on the planet.
It seems incredible how life can bounce back after a disaster. These cataclysms have proven to be vital in the evolution of species on the planet.
When did humans first appear on earth?
Here the story of earth gets very complicated. By now, life is very diverse across the globe. There are many opinions and ideas concerning the first humans, their evolution and spread over the world.
It is agreed that our earliest ancestors diverged from chimpanzees sometime around 6 million years ago. There some say this number may vary between 5-7 million years.
Sometime after that, the earliest hominins began walking on two feet, and our ancestors started the evolutionary journey towards modern humans.
Conclusion
The story of earth begins 4.6 million years ago and takes a journey of difficulty and resilience.
Today most of what we know is a scientific guess. In the coming years it’s likely we will see this story change.
We can thank our lives today for the process of planet earth.
Now it’s up to you. What will we learn of the way our earth formed?
Leave your thoughts in the comment section below.
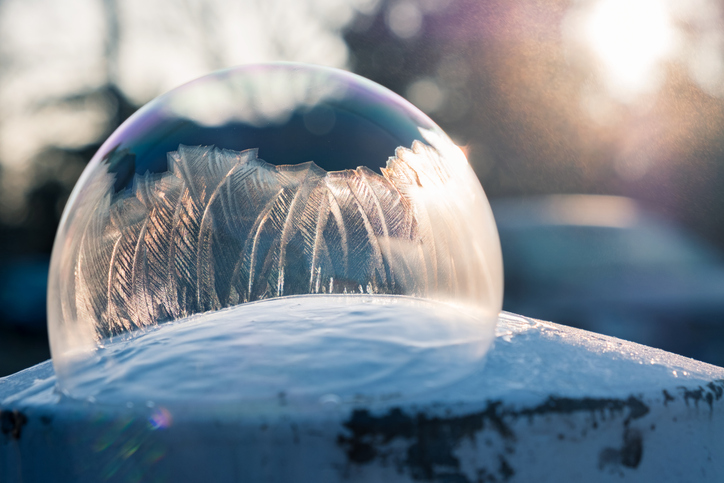

 The story of earth is one of drama and intrigue.
The story of earth is one of drama and intrigue.